A Simple, Clear Guide to Understanding U.S. Immigration Status
Many people use the words “green card” and “visa” as if they mean the same thing. But they are very different.
If you are planning to travel, study, work, or live in the United States, it is important to understand the difference between a green card and a visa. One allows you to enter the country for a limited time. The other allows you to live there permanently.
In this article, we explain everything in simple and clear language so you can fully understand how each one works.
What Is a Visa?
A visa is a document placed inside your passport. It allows you to travel to the United States and request permission to enter.
It does not automatically allow you to stay forever.
Visas are issued by U.S. embassies and consulates in other countries. When you arrive at a U.S. airport or border, an immigration officer decides how long you can stay.
Two Main Types of Visas
There are two major visa categories:
1. Nonimmigrant Visa (Temporary Stay)
This type of visa is for people who want to stay in the U.S. for a limited time.
Examples include:
-
Tourist visas (B1/B2)
-
Student visas (F-1)
-
Work visas (H-1B)
-
Exchange visitor visas (J-1)
If you have a temporary visa, you must leave the U.S. when your authorized stay ends.
2. Immigrant Visa (Permanent Intent)
An immigrant visa is for people who plan to live permanently in the United States.
After entering the U.S. with an immigrant visa, you typically receive a green card.
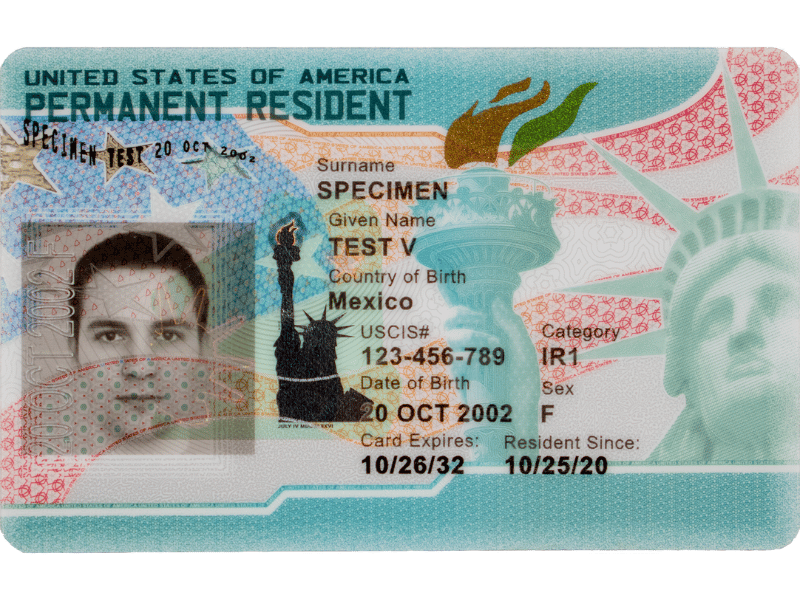
What Is a Green Card?
A green card is officially called a Permanent Resident Card.
It proves that you are a lawful permanent resident of the United States.
Unlike a visa, a green card allows you to:
-
Live in the U.S. permanently
-
Work legally without special permission
-
Travel in and out of the country (with some limits)
-
Apply for U.S. citizenship after a few years
A green card is issued by the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
The Main Difference Between a Green Card and a Visa
Here is the simple explanation:
| Visa | Green Card |
|---|---|
| Allows temporary stay (in most cases) | Allows permanent residence |
| Placed inside passport | Separate physical card |
| Has an expiration date | Valid long-term (usually 10 years, renewable) |
| Does not give permanent rights | Gives legal permanent resident status |
| Must follow strict time limits | Can live and work freely in the U.S. |
In short:
👉 A visa helps you enter the United States.
👉 A green card allows you to live there permanently.
How Long Can You Stay?
With a Visa

Your stay depends on your visa type.
For example:
-
Tourist visa: Usually up to 6 months
-
Student visa: As long as you are enrolled in school
-
Work visa: Based on your employment contract
When your authorized stay ends, you must leave unless you apply for an extension.
With a Green Card
You can live in the U.S. permanently.
However, if you stay outside the U.S. for too long (usually more than 6–12 months), you may risk losing your permanent resident status.
Can a Visa Turn Into a Green Card?
Yes, sometimes.
This process is called Adjustment of Status.
For example:
-
A student on an F-1 visa may get sponsored by an employer.
-
A tourist may marry a U.S. citizen.
-
A worker may qualify for employment-based permanent residency.
After approval, the person receives a green card and becomes a permanent resident.
But not all visas allow easy transition. Some have strict rules.
Rights and Benefits Comparison
Let’s look at the differences more clearly.
Visa Holders
Visa holders can:
-
Enter the U.S. for a specific reason
-
Stay temporarily
-
Study or work (if visa allows)
Visa holders cannot:
-
Vote
-
Stay permanently (unless approved for green card)
-
Receive most federal benefits
Green Card Holders
Green card holders can:
-
Live anywhere in the U.S.
-
Work for almost any employer
-
Start a business
-
Sponsor certain family members
-
Apply for citizenship after 3–5 years
They still cannot vote in federal elections.
Different Ways to Get a Visa
To get a visa, you must:
-
Apply online
-
Pay the visa fee
-
Attend an interview at a U.S. embassy
-
Provide documents (passport, photos, proof of funds, etc.)
The officer decides whether to approve or deny the visa.
Approval depends on:
-
Purpose of travel
-
Financial support
-
Ties to your home country
-
Background check
Different Ways to Get a Green Card
There are several ways to become a permanent resident.
1. Family-Based Green Card
If you have close relatives who are U.S. citizens or permanent residents, they may sponsor you.
2. Employment-Based Green Card
Some workers qualify through employer sponsorship.
3. Diversity Visa Lottery
The U.S. Department of State runs the Diversity Visa Lottery each year. It gives green cards to people from countries with low immigration rates to the U.S.
4. Refugee or Asylum Status
Refugees and asylum seekers may apply for a green card after one year in the U.S.
Travel Differences
Traveling With a Visa
If you leave the U.S., you may need:
-
A valid visa
-
A valid passport
-
Proof you are still eligible
If your visa expires while abroad, you must reapply.
Traveling With a Green Card
Green card holders can travel more freely.
However:
-
Trips longer than 6 months can raise questions.
-
Trips longer than 1 year may require a reentry permit.
Taxes and Responsibilities
Both visa holders and green card holders may have U.S. tax obligations.
Green card holders are considered U.S. tax residents. This means they must report worldwide income.
Visa holders may also need to file taxes, depending on their visa type and income.
Permanent residents must also:
-
Carry their green card at all times
-
Follow U.S. laws
-
Update USCIS when they change address
Which One Do You Need?
It depends on your goal.
You Need a Visa If:
-
You want to visit the U.S. temporarily
-
You plan to study for a limited time
-
You have a short-term job
You Need a Green Card If:
-
You want to live permanently in the United States
-
You want long-term job freedom
-
You plan to become a U.S. citizen in the future
Common Misunderstandings
Myth 1: A Visa Means You Can Stay Forever
False. Most visas are temporary.
Myth 2: A Green Card Makes You a Citizen
False. A green card gives permanent residency, not citizenship.
Myth 3: Getting a Green Card Is Fast
Not always. Some categories take years due to waiting lists.
Green Card vs Visa: Quick Summary
Here is the easiest way to remember:
-
A visa is permission to enter temporarily.
-
A green card is permission to live permanently.
Think of it this way:
A visa is like a temporary visitor pass.
A green card is like becoming a permanent member.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between a green card and a visa is very important before making any immigration decision.
A visa is usually your first step if you want to visit, study, or work in the United States temporarily.
A green card is the next level. It allows you to build a permanent life in the country.
Each option has its own rules, benefits, and responsibilities. Always check official information from the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services or speak with a qualified immigration professional before applying.